|
|
Dynamic Memory Allocation(malloc and calloc).
King Chapter 17: describes the mechanism for obtaining a
pointer to a block of new memory. This is accomplished
with the routines, mallocand calloc, found in <stdlib.h>
malloc()returns N bytes of space for the user, and
calloc()gets space for an array of objects each of size N.
Thus malloc is best viewed as returning a pointer to an
array of chars, while calloc will return a pointer to an
array of the same type as the objects in each element.
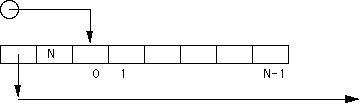
int N = 100;
char* p = (char*) malloc (N);
will return a pointer to a space in the heap were a
contiguous block of 100 bytes of memory exists. NONE of
those bytes will be initialized. If space cannot be found,
then p will be NULL.
However, keep in mind that to manage this memory the
system actually needs some overhead space.
p
|
|
|

 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10