functions
function
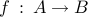
f (rule/map) from A (domain) to B (range)
dot/line diagram
dots for domain
dots for range
(dot x) — (dot y) iff f:x→y
as one-line notation sequence
eg. A = { a, b, c, d, e } B = { 3, 7, 9 }
order elements of domain, eg. a b c d e
write vector ( f(a), f(b), f(c), f(d), f(e) ), eg. (7, 7, 3, 9, 7)
counting functions
= |B||A|
proof
number of |A|-sequences of an |B|-set
types of function f:A to B
for every b in B, exists ≥ one a in A, f(a) = b
onto
for every b in B, exists ≤ one a, f(a) = b
one-to-one (better: at-most-one - to - one)
for every b in B, exists exactly one a, f(a) = b
iff surjection and injection
matching
partitions
set P of subsets of S
each element of P, called a block, is non-empty
each element of S in exactly one element of P
e.g. S = { a b c d e }
P = { { a } { c } { b d e } }
Q = { { a } { c } { d e } } is not a partition of S
R = { { a } { c } { a d e } } is not a partition of S
S(n,0) = 0 (why ?)
for n ≥ 1, S(n,1) = S(n,n) = 1 (why ?)
for n > k > 1: pick element x of S
number k-partitions with block { x } = S(n-1,k-1)
number k-partitions with block { x , … } = kS(n-1,k)
for n > k > 1: S(n,k) = S(n-1,k-1) + k S(n-1,k)
n\k 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ... 0 0 ... 1 0 1 ... 2 0 1 1 ... 3 0 1 3 1 ... 4 0 1 7 6 1 ... 5 0 1 15 25 10 1 ... 6 0 1 31 90 65 15 1 ... 7 0 1 63 301 350 140 21 1 ...
counting functions by image size
image of f:A to B set { b ∈ B | ∃ a ∈ A, f(a) = b }
coimage of f:A to B partition { f-1(b) | b ∈ image(f) }
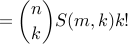
pick image:
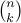
pick coimage: S(m,k)
match coimage blocks ↔ image elements: k!
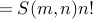
why ?
surjection, so size of image = n
previous formula, k=n
eg. number of surjections from 6-set to 4-set is S(6,4)4!=1560
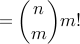
why ?
injection, so size of image = m (and so
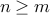 )
)previous formula, k=m
eg. number of injections from 4-set to 6-set is C(6,4)4!=360
function composition
composition of permutations
permutation p of A = { 1 … n } is function p:A to A
e.g. let p = (1 3 5 2 4) (function in one-line form)
pp = (? ? ? ? ?)
pp(1) = p(p(1)) = p(1) = 1
pp(2) = p(p(2)) = p(3) = 5
pp(3) = p(p(3)) = p(5) = 4
pp(4) = p(p(4)) = p(2) = 3
pp(5) = p(p(5)) = p(4) = 2
so pp = (1 5 4 3 2)
p-1 = (? ? ? ? ?)
p(?) = 1 ?=1 so p-1(1) = 1
p(?) = 2 ?=4 so p-1(2) = 4
p(?) = 3 ?=2 so p-1(2) = 2
p(?) = 4 ?=5 so p-1(2) = 5
p(?) = 5 ?=3 so p-1(2) = 3
so p-1 = (1 4 2 5 3)
permutation: cyclic form
for permutation p:A to A, for every element a, sequence (a p(a) pp(a) ppp(a) … ) eventually cycles
e.g. p = (1 3 5 2 4)
(1)
(2 3 5 4)
(3 5 4 2)
(5 4 2 3)
(4 2 3 5)
so permutation is often described in cyclic form
one-line form cyclic form (1 2 3) (1) (2) (3) (1 3 2) (1) (2 3) (2 3 1) (1 2 3) (1 3 5 2 4) (1) (2 3 5 4) (9 10 8 7 3 1 4 2 6 5) (1 9 6) (2 10 5 3 8) (4 7)
permutation order
let p = (1) (2 3 5 4) cyclic form
p0 = (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) identity permutation
p1 = (1) (2 3 5 4)
p2 = (1) (2 5) (3 4)
p3 = (1) (2 4 5 3)
p4 = (1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
p5 = p4 p1 = p
p6 = p4 p2 = p2
p7 = p4 p3 = p3
p8 = p4 p4 = (1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
etc
order of permutation p = smallest positive integer t, pt = identity
def addone(p):
for j in range(len(p)): p[j]+=1
return p
def permpower(p,t):
q = []
for j in range(len(p)): q.append(j)
if t==0: return q
for j in range(len(p)):
indx = j
for _ in range(t): indx = p[indx]-1
q[j] = indx
return q
#p = [9, 10, 8, 7, 3, 1, 4, 2, 6, 5]
p = [3,1,4,2]
print 'perm ',p
for t in range(5):
print 'power',t,':', addone(permpower(p,t))
e.g. p = (9 10 8 7 3 1 4 2 6 5) one-line form
hint: find cyclic form of p
(9 10 8 7 3 1 4 2 6 5) (1 9 6) (2 10 5 3 8) (4 7)
01 (1 9 6) (2 0 5 3 8) (4 7) 02 (1 6 9) (2 5 8 0 3) (4)(7) 03 (1)(6)(9) (2 3 0 8 5) (4 7) 04 (1 9 6) (2 8 3 5 0) (4)(7) 05 (1 6 9) (2)(3)(5)(8)(0) (4 7) 06 (1)(6)(9) (2 0 5 3 8) (4)(7) .. ......... ............... ...... ?? (1)(6)(9) (2)(3)(5)(8)(0) (4)(7)