computer arithmetic
computer arithmetic
- computers use binary arithmetic
- positional number systems
binary (2) octal (8) decimal (10) hexadecimal (16: digits 0 … 9 A … F}
positional number systems
- decimal (10)
6270310 =
6 × 104 +
2 × 103 +
7 × 102 +
0 × 101 +
3 × 100
- binary (2)
1010012 =
1 × 25 +
0 × 24 +
1 × 23 +
0 × 22 +
0 × 21 +
1 × 20
- base b
(ad-1ad-2...a1a0)b =
ad-1 × bd-1 +
ad-2 × bd-2 +
. . . +
a1 × b1 +
a0 × b0
convert decimal to base b
repeat: divide by b, take remainder
| 217 | = | 2 | × | 108 | + | 1 |
| 108 | = | 2 | × | 54 | + | 0 |
| 54 | = | 2 | × | 27 | + | 0 |
| 27 | = | 2 | × | 13 | + | 1 |
| 13 | = | 2 | × | 6 | + | 1 |
| 6 | = | 2 | × | 3 | + | 0 |
| 3 | = | 2 | × | 1 | + | 1 |
| 1 | = | 2 | × | 0 | + | 1 |
21710 = 110110012
check ? convert back (see below)
convert base b to decimal
n <- most sig. digit while digits remain: n <- n*b + next digit
| 110110012 ? | |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 × 2 + 1 | 3 |
| 3 × 2 + 0 | 6 |
| 6 × 2 + 1 | 13 |
| 13 × 2 + 1 | 27 |
| 27 × 2 + 0 | 54 |
| 54 × 2 + 0 | 108 |
| 108 × 2 + 1 | 217 |
check with web calculator:
1 + 2 * (0 + 2 * (0 + 2 * (1 + 2 * (1 + 2 * (0 + 2 * (1 + 2 * (1) ) ) ) ) ) ) = 21710
| 6253017 ? | |
| 6 | 6 |
| 6 × 7 + 2 | 44 |
| 44 × 7 + 5 | 313 |
| 313 × 7 + 3 | 2194 |
| 2194 × 7 + 0 | 15358 |
| 15358 × 7 + 1 | 107507 |
1 + 7 * (0 + 7 * (3 + 7 * (5 + 7 * (2 + 7 * (6) ) ) ) ) ) = 10750710
convert binary to hexadecimal
16=24, so start at least sig. bit, group each 4 bits
10100111100110101002 =
101 0011 1100 1101 0100 =
5 3 C D 416
binary arithmetic
use algorithms from elementary school
1101 0110 + 101 0011 = ?
1101 0110 – 101 0011 = ?
1101 0110 × 101 0011 = ?
1101 0110 / 1001 = ?
1 1 11 00
1101 0110 1101 0110
+ 101 0011 - 101 0011
----------- -----------
1 0010 1001 1000 0011
11010110
* 1010011
----------
11010110
11010110
11010110
+ 11010110
----------------
100010101100010
10111
--------
1001 | 11010110
1001
----
1000
0000
----
10001
1001
----
10001
1001
----
10000
1001
----
0111
n-bit registers
register
arithmetic: special-purpose ⇒ small
4-bit: 0000 to 1111 ⇒ 24 numbers
8-bit: 0000 0000 to 1111 1111 ⇒ 28 numbers
n-bit: 000…0 to 111…1 ⇒ 2n numbers
fixed-size ⇒ can overflow
4-bit: 1101 + 0111 = 0100 ⇒ arith. mod 24
8-bit: 1111 1111 + 0000 0001 = 0000 0000 ⇒ arith. mod 28
n-bit: ⇒ arith. mod 2n
neg. numbers: 2's-complement
how to get n-bit pos. and neg. numbers ? (arith mod 2n)
-x (mod 2n) = 2n -x (mod 2n)
so, pick positive/negative numbers
negative: leading bit 1
⇒ negatives: -2n-1 . . . -1
⇒ positives: 1 . . . 2n-1-1
0000 0 0 0001 1 1 0010 2 2 0011 3 3 0100 4 4 0101 5 5 0110 6 6 0111 7 7 1000 8 -8 1001 9 -7 1010 10 -6 1011 11 -5 1100 12 -4 1101 13 -3 1110 14 -2 1111 15 -1
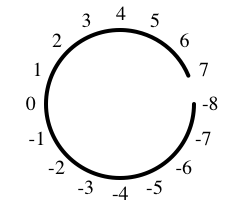
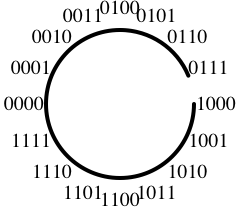
2's-complement arithmetic
- negate(x)
= 2n – x
= 2n–1 –x + 1
= flip_bits(x) + 1- overflow ?
only if x = –2n-1 (why?)
neg( 0010 1010 ) neg( 1101 0110 ) = 1101 0101 + 1 = 0010 1001 + 1 = 1101 0110 = 0010 1010
- x + y
usual method: + (mod 2n)
- overflow ?
only if sign(x) = sign(y) ≠ sign(x+y) (why?)
1011 1010 1011 0110 1011 0111 + 1101 1101 + 0101 1101 + 1001 1011 --------- --------- --------- 1001 0111 0001 0011 0101 0010
- x – y
= x + negate(y)