graphs: decompositions
D A -- C B -- H
| \ | \ |
| \ | \ |
E -- F G
nodes A B C D E F G H
degrees 3 2 2 0 2 3 2 2
edges 8
sum of degrees 16
G = (V,E)
graph, vertex/node/point, edge/line
adjacent
subgraph
connected
component: maximal connected subgraph
degree of a vertex
n or |V| number of nodes
m or |E| number of edges
graph representation
adjacency matrix
A B C D E F G H
A 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0
B 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
C 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
D 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
E 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
F 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
G 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
H 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
adjacency list
A [C E F]
B [H G]
C [A F]
D [ ]
E [A F]
F [A C E]
G [B H]
H [B G]
adjacency matrix uses n2 bits
adjacency list uses n + 2m node labels
worst case, m ∈ Θ( n2 )
if n large and average degree small, lists smaller than matrix
graph traversal: depth first search
def dfs(G):
seen = {}
for v in G: seen[v] = False
for v in G:
if not seen[v]:
explore(G,v,seen)
def explore(G,v,seen):
print v, 'start explore'
seen[v] = True
for nbr in G[v]:
if not seen[nbr]:
explore(G,nbr,seen)
print v, 'finish explore'
def show(G):
for v in sorted(G):
print v,':',
for j in G[v]: print j,
print ''
print ''
G = {'A': ['C', 'E', 'F'],
'B': ['G', 'H'],
'C': ['A', 'F'],
'D': [],
'E': ['A', 'F'],
'F': ['A', 'C', 'E'],
'G': ['B', 'H'],
'H': ['B', 'G']}
show(G)
dfs(G)
A start explore C start explore F start explore E start explore E finish explore F finish explore C finish explore A finish explore B start explore G start explore H start explore H finish explore G finish explore B finish explore D start explore D finish explore
preorder: by dfs start (1st encounter)
A C F E B G H D
postorder: by dfs finish (last encounter)
E F C A H G B D
components
def dfs(G):
pre,post,seen,cmpt = {},{},{},{}
for v in G:
seen[v] = False
clock, cnum = [0], 0 #clock[0] passed by ref
for v in G:
if not seen[v]:
cnum += 1
explore(G,v,seen,pre,post,clock,cmpt,cnum)
showall(G,pre,post,cmpt)
def explore(G,v,seen,pre,post,clock,cmpt,c):
print 'explore from', v
seen[v] = True
cmpt[v] = c
timestamp(v, pre, clock)
for nbr in G[v]:
if not seen[nbr]:
explore(G,nbr,seen,pre,post,clock,cmpt,c)
timestamp(v, post, clock)
def timestamp(v, order, clock):
clock[0]+= 1; order[v] = clock[0]
def showall(G,pre,post,cnum):
print ' ',
for v in sorted(G): print '%2s' % v,
print '\npre ',
for v in sorted(G): print '%2s' % pre[v],
print '\npost ',
for v in sorted(G): print '%2s' % post[v],
print '\ncmpt ',
for v in sorted(G): print '%2s' % cnum[v],
def show(G):
for v in sorted(G):
print v,':',
for j in G[v]: print j,
print ''
print ''
G = {'A': ['C', 'E', 'F'],
'B': ['G', 'H'],
'C': ['A', 'F'],
'D': [],
'E': ['A', 'F'],
'F': ['A', 'C', 'E'],
'G': ['B', 'H'],
'H': ['B', 'G'] }
show(G)
dfs(G)
traversal runtime
adjacency matrix:
adjacency list:
why? see text, then guess output from examples below
def traverse(G):
seen,cmpt,cnum,work = {},{},0,[0] #work reflects runtime
for v in G:
seen[v] = False
cmpt[v] = 0
for v in sorted(G):
work[0] += 1
if not seen[v]:
cnum += 1
dfs(G,v,seen,cmpt,cnum,work)
print ''
for v in sorted(G): print v,
print ''
for v in sorted(G): print cmpt[v],
print '\nwork', work[0]
def dfs(G,v,seen,cmpt,c,work):
seen[v],cmpt[v],work[0] = True,c,work[0]+1
for nbr in sorted(G[v]):
work[0] += 1
if not seen[nbr]:
dfs(G,nbr,seen,cmpt,c,work)
print v,
def show(G):
for v in sorted(G):
print v,':',
for j in G[v]: print j,
print ''
print ''
G = {'A': ['F'],
'B': ['D','C'],
'C': ['G','B','E','D'],
'D': ['G','B','C'],
'E': ['C','G'],
'F': ['A'],
'G': ['C', 'D']}
show(G)
traverse(G)
def n(G): return len(G[0])
def alpha(j): return chr(j+ord('A'))
def traverse(G):
seen,cmpt,cnum,work = {},{},0,[0]
for v in range(n(G)):
seen[v] = False
cmpt[v] = 0
for v in range(n(G)):
work[0] += 1
if not seen[v]:
cnum += 1
dfs(G,v,seen,cmpt,cnum,work)
print ''
for v in range(n(G)): print alpha(v),
print ''
for v in range(n(G)): print cmpt[v],
print '\nwork', work[0]
def dfs(G,v,seen,cmpt,c,work):
seen[v],cmpt[v],work[0] = True,c,work[0]+1
for j in range(n(G)): # possible nbr
work[0] += 1
if G[v][j]==1: # j is nbr
if not seen[j]:
dfs(G,j,seen,cmpt,c,work)
print alpha(v),
def show(G):
print ' ',
for v in range(n(G)): print alpha(v),
print ''
for v in range(n(G)):
print alpha(v),':',
for w in range(n(G)):
if G[v][w]==1: print '1',
else: print '0',
print ''
print ''
G = ([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0])
show(G)
traverse(G)
breadth first search
B - L - G M A
\ / \ / \ /
I - E H - K
\ / \
C - J - F - D
def bfs(G): # depth in bfs forest
seen, depth = {}, {}
for v in G:
seen[v], depth[v] = False, 0
print 'bfs order ',
for v in sorted(G):
if not seen[v]:
explorebfs(G,v,seen,depth)
print '\nnodes ',
for v in sorted(G): print v,
print '\nbfs forest depth',
for v in sorted(G): print depth[v],
print ''
def addtolist(L,v,seen):
L.append(v); seen[v]=True
def explorebfs(G,v,seen,d):
Q = []
addtolist(Q,v,seen)
while len(Q)>0:
v = Q.pop(0); print v,
for nbr in G[v]:
if not seen[nbr]:
d[nbr] = 1 + d[v]
addtolist(Q,nbr,seen)
def show(G):
for v in sorted(G):
print v,':',
for j in G[v]: print j,
print ''
G = { 'A':['H'],
'B':['I','L'],
'C':['E','I','J'],
'D':['F'],
'E':['C','G','I','J','L'],
'F':['D','J'],
'G':['E','L'],
'H':['A','K','M'],
'I':['B','C','E','L'],
'J':['C','E','F'],
'K':['H'],
'L':['B','E','G','I'],
'M':['H']}
bfs(G)
directed graphs
D = { 'A':['B'],
'B':['C','E','F'],
'C':['D','G'],
'D':['C','H'],
'E':['A','F'],
'F':['G'],
'G':['F'],
'H':['D','G']
}
arc
strongly connected: if, for each ordered pair of vertices (a,b), there is a path from a to b
strongly connected component:
vertex subset
the subset is strongly connected
the subset is maximal (wrt being strongly connected)
transpose of a digraph: reverse direction of every arc
in a digraph
source node/scc: has no in-arcs
sink node/scc: has no out-arcs
strongly connected components
to find sccs of digraph D:
find node s in sink scc S
find and remove S
repeat until done
how to find s ?
last in postorder of transpose T
how to find S?
start from s, use dfs/bfs on D
runtime
adjacency list
can find transpose in Θ(n+m) time
total Θ(n+m) time
adjacency matrix
can find transpose in time Θ(n2)
total time Θ(n2)
correctness
in acyclic digraph D postorder
each v appears after all w reachable from v, so
last vertex is D source, so
in transpose T postorder
last vertex is T source, so
last vertex is D sink
in postorder of transpose T of arbitrary digraph D,
last vertex is in D sink scc
def dfs(G,v,seen,cmpt,c,S,phase):
seen[v],cmpt[v] = True,c
for nbr in sorted(G[v]):
if not seen[nbr]: dfs(G,nbr,seen,cmpt,c,S,phase)
if (phase==0): S.append(v) # append in postorder
def transpose(G):
T = {}
for v in G: T[v] = []
for v in G:
for w in G[v]: T[w].append(v)
return T
def scc(G):
phase,seen,cmpt,c,S = 0,{},{},0,[]
for v in G: seen[v],cmpt[v] = False, 0
T = transpose(G)
for v in sorted(T):
if not seen[v]: dfs(T,v,seen,cmpt,c,S,phase)
showall(T,cmpt,S)
phase,c = 1,0
for v in G: seen[v],cmpt[v] = False, 0
while len(S)>0:
v = S.pop() # pop from end, so reverse order
if not seen[v]:
c += 1
dfs(G,v,seen,cmpt,c,S,phase)
showall(G,cmpt,S)
def showall(G,cmpt,S):
print ' ',
for v in sorted(G): print '%2s' % v,
print '\ncmpt ',
for v in sorted(G): print '%2s' % cmpt[v],
print '\nstack', S
D = { 'A':['B'],
'B':['C','E','F'],
'C':['D','G'],
'D':['C','H'],
'E':['A','F'],
'F':['G'],
'G':['F'],
'H':['D','G']
}
G = {'A':['F'],
'B':['H'],
'C':['B','F'],
'D':['I'],
'E':['B'],
'F':['C','I'],
'G':['E'],
'H':['G'],
'I':['A','G']}
scc(D)
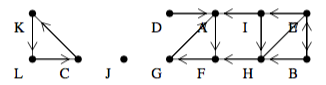
a digraph D
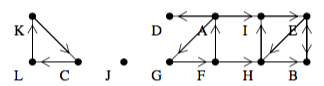
its transpose T
D dfs traversal forest:
A C J
D G L
F K
H
B I
E
D-dfs postorder
D E B I H F G A K L C J
notice:
postorder-first node in sink scc (why?)
postorder-last node in source scc (why?)
T dfs traversal forest:
A B C D J
F E K
G I L
H
T-dfs postorder
G F A H I E B L K C D J
G dfs traversal forest, using reverse T postorder:
J D C B A
K E F
L I G
H
notice:
each tree in above forest is scc of T/D
how do the results of scc(D) compare with scc(transpose(D)) ?
try an example or two
explain